8 Form Controls
XForms User Interface controls—form
controls—are declared using markup elements, and their behavior
refined via markup attributes. This markup may be decorated with
class attributes that can be used in CSS stylesheets to deliver a
customized look and feel. XForms user interface controls are bound to the
underlying instance data using binding
attributes as defined in the chapter 6 Constraints.
Form controls enable accessibility by taking a uniform approach to such features as captions, help text, tabbing and keyboard shortcuts. Internationalization issues are addressed by following the same design principles as in XHTML. All form controls are suitable for styling using Aural CSS (ACSS) style properties.
Form controls encapsulate high-level semantics without sacrificing the
ability to deliver real implementations. For instance, form controls
selectOne and selectMany enable the user select one or
more items from a set. These form controls distinguish the functional
aspects of the underlying control from the presentational aspects (through
class attributes) and behavior (through XForms Action elements).
This separation enables the expression of the intent underlying a particular
form control—see [AUI97] for a
definition of such high-level user interaction
primitives.
Form controls when rendered display the underlying data values to which they are bound. While the data presented to the user through a form control must directly correspond to the bound instance data, the display representation is not required to exactly match the lexical value. For example, user agents should apply appropriate conventions to the display of dates, times, durations and numeric values including separator characters.
XForms user interface controls use common attributes and elements that are defined in (8.12 Common Markup ). Sections in this chapter define the various form controls by specifying the following:
Description
Examples
Data Binding Restrictions
Implementation Requirements
XML Representation
8.1 input
Description: This form control enables free-form data entry.
<input ref="order/shipTo/street" class="streetAddress"> <caption>Street</caption> <hint>Please enter the number and street name</hint> </input>
In the above, the class attribute can be used by a
stylesheet to specify the display size of the form control. Note that the
constraints on how much text can be input are obtained from the underlying
XForms Model definition and not from these display properties.
A graphical browser might render the above example as follows:

Data Binding Restrictions: Binds to any simpleContent (except xsd:base64Binary, xsd:hexBinary or any datatype derived from these).
Implementation Requirements: Must allow entry of a lexical value for the
bound datatype. Implementations should provide the most convenient means
possible for entry of datatypes and take into account localization and
internationalization issues such as representation of numbers. For example, an
input bound to an instance data node of type Date might provide a calendar control to enter dates; similarly, an input
control bound to data instance of type boolean might be rendered as a simple checkbox.
input><input (single node binding attributes) (common attributes) inputMode = xsd:string > <!-- caption, (help|hint|alert|action|extension)* --> </input>
(single node binding attributes) - Selection of instance data node, defined in 8.12.2 Single Node Binding Attributes
common attributes defined in 8.12.1 Common Attributes
inputMode - this form control accepts an input mode hint. D Input Modes
Note:
Notice that not binding any user interface to a piece of
instance data results in an hidden form control in XForms;
consequently, there is no need to explicitly define input form controls with type="hidden" as in HTML.
8.2 secret
Description: This form control is used for entering information that is considered sensitive, and thus not echoed to a visual or aural display as it is being entered, e.g., password entry.
<secret ref="/login/password">
<caption>Password</caption>
<hint>Please enter your password --it will not
be visible as you type.</hint>
</secret>A graphical browser might render this form control as follows:
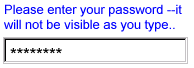
Data Binding Restrictions: Identical to input.
Implementation Requirements: In general, implementations, including accessibility aids, must render a "*" or similar character instead of the actual characters entered, and thus must not render the entered value of this form control. Note that this provides only a casual level of security; truly sensitive information will require additional security measures outside the scope of XForms.
secret><secret (single node binding attributes) (common attributes) inputMode = xsd:string > <!-- caption, (help|hint|alert|action|extension)* --> </secret>
(single node binding attributes) - Selection of instance data node, defined in 8.12.2 Single Node Binding Attributes
common attributes defined in 8.12.1 Common Attributes
inputMode - this form control accepts an input mode hint. D Input Modes
8.3 textarea
Description: This form control enables free-form data entry and is intended for use in entering multiline content, e.g., the body of an email message.
<textarea ref="message/body" class="messageBody"> <caption>Message Body</caption> <hint>Enter the text of your message here</hint> </textarea>
In the above, the class attribute can be used by a
stylesheet to specify the display size of the form control. Note that the
constraints on how much text can be input are obtained from the underlying
XForms Model definition and not from these display properties.
A graphical browser might render the above example as follows:

Data Binding Restrictions: Binds to xsd:string or any derived simpleContent.
Implementation Requirements: Must allow entry of a lexical value for the bound datatype, including multiple lines of text.
textarea><textarea (single node binding attributes) (common attributes) inputMode = xsd:string > <!-- caption, (help|hint|alert|action|extension)* --> </textarea>
(single node binding attributes) - Selection of instance data node, defined in 8.12.2 Single Node Binding Attributes
common attributes defined in 8.12.1 Common Attributes
inputMode - this form control accepts an input mode hint. D Input Modes
8.4 output
Description: This form control renders a value from the instance data,
but provides no means for entering or changing data. It is typically used to
display values from the instance, and is treated as display:inline for purposes of layout.
I charged you - <output ref="order/totalPrice"/> and here is why:
A graphical browser might render an output form control as follows:

Data Binding Restrictions: Binds to any simpleContent.
Implementation Requirements: Must allow display of a lexical value for the bound datatype. Implementations should provide the most convenient means possible for display of datatypes and take into account localization and internationalization issues such as representation of numbers.
output><output (single node binding attributes) > <!-- empty content --> </output>
(single node binding attributes) - Selection of instance data node, defined in 8.12.2 Single Node Binding Attributes
8.5 upload
Description: This form control enables the common feature found on Web sites to upload a file from the local file system, as well as accepting input from various devices including microphones, pens, and digital cameras.
<upload ref="mail/attach1" mediaType="image/*"> <caption>Select image:</caption> </upload>
A graphical browser might render this form control as follows:
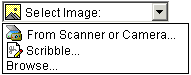
Data Binding Restrictions: This form control can only be bound to
datatypes xsd:base64Binary or xsd:hexBinary, or types derived by restriction from these.
Implementation Requirements: For suitable mediaTypes:
Implementations with a file system should support file upload—selecting a specific file. The types of files presented by default must reflect the mediaType specified in the XForms Model, for example defaulting to only audio file types in the file dialog when the mediaType is "audio/*". In XForms 1.0, there is a 1:1 binding between a upload form control and one of the
binarydatatypes, although that single file may be compound (e.g. application/zip).Implementations with specific pen/digitizer hardware should (and implementations with other pointing devices may) support scribble—allowing in-place creation of pen-based data.
Implementations with specific audio recording capabilities should support record audio—in-place recording of an audio clip.
Implementations with a digital camera/scanner interface or screen capture should support acquire image—in-place upload of images from an attached device.
Implementations with video recording capability should provide a record video option.
Implementations with 3d capabilities should provide a 3d interface option.
Implementations may provide proprietary implementations (for example, a mediaType of text/rtf could invoke an edit window with a proprietary word processing application)
Implementations are encouraged to support other input devices not mentioned here.
Implementations which cannot support upload for the given mediaType must make this apparent to the user.
upload><upload (single node binding attributes) (common attributes) mediaType = list of content types > <!-- caption, (help|hint|alert|action|extension)* --> </upload>
(single node binding attributes) - Selection of instance data node, defined in 8.12.2 Single Node Binding Attributes
common attributes defined in 8.12.1 Common Attributes
mediaType - list of suggested media types, used by the XForms Processor to determine which input methods apply.
8.6 range
Description: This form control allows selection from a continuous range of values.
<range ref="/stats/balance" start="-2.0" end="2.0" stepSize="0.5"> <caption>Balance</caption> </range>
A graphical browser might render this as follows:
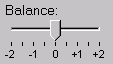
Data Binding Restrictions: Binds only the following list of datatypes,
or datatypes derived by restriction from those in the list: xsd:duration, xsd:date, xsd:time, xsd:dateTime, xsd:gYearMonth, xsd:gYear, xsd:gMonthDay, xsd:gDay, xsd:gMonth, xsd:float, xsd:decimal, xsd:double.
Implementation Requirements: Must allow input of a value corresponding to the bound datatype. Implementations should inform the user of the upper and lower bounds, as well as the step size, if any. In graphical environments, this form control may be rendered as a "slider" or "rotary control".
Notice that the attributes of this element encapsulate sufficient metadata that in conjunction with the type information available from the XForms Model proves sufficient to produce meaningful prompts when using modalities such as speech, e.g., when using an accessibility aid. Thus, an aural user agent might speak a prompt of the form Please pick a date in the range January 1, 2001 through December 31, 2001.
range><range (single node binding attributes) (common attributes) start = datavalue end = datavalue stepSize = datavalue-difference > <!-- caption, (help|hint|alert|action|extension)* --> </range>
(single node binding attributes) - Selection of instance data node, defined in 8.12.2 Single Node Binding Attributes
common attributes defined in 8.12.1 Common Attributes
start - optional hint for the lexical starting bound for the range—a legal value for the underlying data.
end - optional hint for the ending bound for the range—a legal value for the underlying data.
stepSize - optional hint to use for incrementing or decrementing the value. Should be of a type capable of expressing the difference between two legal values of the underlying data.
8.7 button
Description: This form control is similar to the HTML element of the same name and allows for user-triggered actions. This form control may also be used to advantage in realizing other custom form controls.
<button> <caption>Click here</caption> </button>
Data Binding Restrictions: Binding not possible for this form control.
Implementation Requirements: The user agent must provide a means to
generate an xforms:activate event on the form control. Graphical implementations would typically
render this form control as a push-button with the caption on the button face.
Stylesheets can be used to style the button as an image.
button><button (common attributes) > <!-- caption, (help|hint|alert|action|extension)* --> </button>
common attributes defined in 8.12.1 Common Attributes
8.8 submit
Description: This form control initiates submission of all or part of the instance data to which it is bound.
<submit submitInfo="timecard"> <caption>Submit Timecard</caption> </submit>
Data Binding Restrictions: Binding not possible for this form control.
Implementation Requirements: Upon receiving event xforms:activate, this form control dispatches event xforms:submit to the submitInfo element specified by required attribute submitInfo.
submit><submit (common attributes) submitInfo = xsd:IDREF #REQUIRED > <!-- caption, (help|hint|alert|action|extension)* --> </submit>
submitInfo - Required reference to element
submitInfo
common attributes defined in 8.12.1 Common Attributes
8.9 selectOne
Description: This form control allows the user to make a single selection from multiple choices.
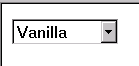
<selectOne ref="my:icecream/my:flavor">
<caption>Flavour</caption>
<item>
<caption>Vanilla</caption>
<value>v</value>
</item>
<item>
<caption>Strawberry</caption>
<value>s</value>
</item>
<item>
<caption>Chocolate</caption>
<value>c</value>
</item>
</selectOne> In the above example, selecting one of the choices will result in the
associated value given by element value on the selected item being set
in the underlying data instance at the location icecream/flavor.
A graphical browser might render this form control as any of the following:
| listbox | checkbox | radio | menu |
|---|---|---|---|

|
 |
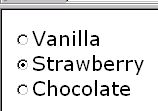
|
 |
Data Binding Restrictions: Binds to any simpleContent.
Implementation Requirements: The caption for each choice must be
presented, allowing at all times exactly one selection. This form control
stores the value corresponding to the selected choice in the location addressed
by attribute ref. The value to be stored is either directly
specified as the contents of element value, or specified indirectly
through attribute ref on element value.
Note that the datatype bound to this form control may include a
non-enumerated value space, e.g., xsd:string. In this case, control selectOne may have attribute
selection="open". The form control should then allow free
data entry, as described in 8.1 input.
For closed selections:If the initial instance value matches the storage value of one of the given items, that item is selected. If there is no match, the first item is initially selected.
For open selections: If the initial instance value matches
the storage value specified by one of the items, the first such matching item
is selected. Otherwise, the selected value is the initial lexical value. Free
entry text is handled the same as form control input
8.1 input.
User interfaces may choose to render this form control as a pulldown list or group of radio buttons, among other options. The selectUI attribute offers a hint as to which rendering might be most appropriate, although any styling information (such as CSS) should take precedence.
Typically, a stylesheet would be used to determine the exact appearance
of form controls, though a means is provided to suggest an appearance through
attribute selectUI. The value of the attribute consists of one of
the following values, each of which may have a platform-specific look and feel.
radio
checkbox
menu
listbox
selectOne><selectOne
(single node binding attributes)
(common attributes)
selectUI = ("radio" | "checkbox" | "menu" | "listbox" )
selection = "open" | "closed" : "closed"
>
<!-- caption, (choices|item|itemset)+, (help|hint|alert|action|extension)* -->
</selectOne>(single node binding attributes) - Selection of instance data node, defined in 8.12.2 Single Node Binding Attributes
common attributes defined in 8.12.1 Common Attributes
selectUI - appearance override
selection - optional attribute determining whether free entry is allowed in the list.
8.10 selectMany
Description: This form control allows the user to make multiple selections from a set of choices.
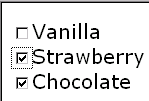
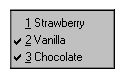
<selectMany ref="my:icecream/my:flavors">
<caption>Flavours</caption>
<choices>
<item>
<caption>Vanilla</caption>
<value>v</value>
</item>
<item>
<caption>Strawberry</caption>
<value>s</value>
</item>
<item>
<caption>Chocolate</caption>
<value>c</value>
</item>
</choices>
</selectMany>In the above example, more than one flavor can be selected.
A graphical browser might render form control selectMany as
any of the following:
| listbox | checkbox | radio | menu |
|---|---|---|---|

|
| This configuration is not recommended. |
|
Data Binding Restrictions: any simpleContent capable of holding a sequence.
Note:
A limitation of the Schema list datatypes is that whitespace
characters in the storage values (the value="..." attribute of the item element) are always interpreted as
separators between individual data values. Therefore, authors should avoid
using whitespace characters within storage values with list simpleContent.
<item> <value>United States of America</value> ... </item>
When selected, this item would introduce not one but four additional selection values: "America", "of", "States", and "United".
Implementation Hints: An accessibility aid might allow the user to browse through the available choices and leverage the grouping of choices in the markup to provide enhanced navigation through long lists of choices.
selectMany><selectMany
(single node binding attributes)
(common attributes)
selectUI = ("radio" | "checkbox" | "menu" | "listbox")
>
<!-- caption, (choices|item|itemset)+, (help|hint|alert|action|extension)* -->
</selectMany>(single node binding attributes) - Selection of instance data node, defined in 8.12.2 Single Node Binding Attributes
common attributes defined in 8.12.1 Common Attributes
selectUI - appearance override
8.11 Common Markup for selection controls
8.11.1 choices
This element is used within selection form controls to group available
choices. This provides the same functionality as element optgroup in
HTML.
choices><choices> <!-- caption?, (choices|item|itemset)+ --> </choices>
8.11.2 item
This element specifies the storage value and caption to represent an
item in a list. It is found within elements selectOne and
selectMany, or grouped in element choices.
item><item> <!-- caption, value, (help|hint|alert|action|extension)* --> </item>
id = xsd:ID - optional unique identifier.
8.11.3 itemset
Element itemset allows the creation of dynamic selections
within controls selectOne and selectMany, where the available
choices are determined at run-time. The node-set that holds the available
choices is specified via attribute nodeset. Child elements
caption and value indirectly specify the caption and storage
values. Notice that the run-time effect of itemset is the same as
using element choices to statically author the available choices.
itemset><itemset (node-set binding attributes) > <!-- caption, value, (help|hint|alert|action|extension)* --> </itemset>
node-set binding attributes - required node-set selector that specifies the node-set holding the available choices.
The following example shows element itemset within control
selectMany to specify a dynamic list of ice cream flavors:
<model id="cone">
<instance>
<my:icecream>
<my:flavours/>
</my:icecream>
</instance>
</model>
<model id="flavours">
<instance>
<my:flavours>
<my:flavour type="v">
<my:description>Vanilla</my:description>
</my:flavour>
<my:flavour type="s">
<my:description>Strawberry</my:description>
</my:flavour>
<my:flavour type="c">
<my:description>Chocolate</my:description>
</my:flavour>
</my:flavours>
</instance>
</model>
<!-- user interaction markup -->
<selectMany model="cone" ref="my:icecream/my:flavours">
<caption>Flavors</caption>
<itemset model="flavours" nodeset="my:flavours/my:flavour">
<caption ref="my:description"/>
<value ref="@type"/>
</itemset>
</selectMany>8.11.4 value
This element provides a storage value to be used when an item
is selected.
Data Binding Restriction: All lexical values must be valid according to the datatype bound to the selection control.
value><value (single node binding attributes) > <!-- ##any --> </value>
single node binding attributes - optional binding selector that specifies a location from where the storage value is to be fetched.
If inline content and a ref attribute are both specified,
the ref attribute is used.
8.12 Common Markup
The preceding form control definitions make reference to child elements and attributes that are common to several of the form controls. This section defines these common markup components.
8.12.1 Common Attributes
The following attributes are common to many user-interface related XForms elements.
xml:lang = xsd:language class = space separated list of classes navIndex = xsd:nonNegativeInteger : 0 accessKey = xsd:token
xml:lang - Optional standard XML attribute to specify a human language for this element.
class - Optional selector for a style rule.
navIndex - Optional attribute is a non-negative integer in the range of 0-32767 used to define the navigation sequence. This gives the author control over the sequence in which form controls are traversed. The default navigation order is specified in the chapter 4 Processing Model.
accessKey - Optional attribute defines a shortcut for moving the input focus directly to a particular form control. The value of this is typically a single character which when pressed together with a platform specific modifier key (e.g., the alt key) results in the focus being set to this form control.
8.12.2 Single Node Binding Attributes
The following attributes define a binding between a form control and an instance data node.
ref = binding-expression model = xsd:IDREF bind = xsd:IDREF
ref - Binding expression. Details in the chapter 6 Constraints. The first-node rule applies to the nodeset selected here.
model - Optional instance data selector. Details in the section 6.4.3 Binding References.
bind - Optional reference to a bind element
It is an error if the model idref value refers to an id not
on a model element, or if the bind idref value refers to an
id not on a bind element.
8.12.3 Nodeset Binding Attributes
The following attributes define a binding between a form control and a node-set returned by the XPath expression.
nodeset = binding-expression model = xsd:IDREF bind = xsd:IDREF
nodeset - Binding expression. Details in the chapter 6 Constraints.
model - Optional instance data selector. Details in the chapter 6 Constraints.
bind - Optional reference to a bind element
It is an error if the model idref value refers to an id not
on a model element, or if the bind idref value refers to an
id not on a bind element.
8.12.4 Common Child Elements
The child elements detailed below provide the ability to attach metadata to form controls.
Instead of supplying such metadata e.g., the label for a form control
as inline content of the contained element caption, the metadata can
be pointed to by using a simple XLink attribute xlink:href on these
elements. Notice that systematic use of this feature can be exploited in
internationalizing XForms user interfaces by:
Factoring all human readable messages to a separate resource XML file.
Using URIs into this XML resource bundle within individual caption elements
Finally, an XForms processor can use content negotiation to obtain the appropriate XML resource bundle, e.g., based on the
accept-languageheaders from the client, to serve up the user interface with messages localized to the client's locale.
8.12.4.1 caption
The required element caption labels the containing form
control with a descriptive label. Additionally, the caption makes it possible
for someone who can't see the form control to obtain a short description while
navigating between form controls.
caption><caption (common attributes) (single node binding attributes) xlink:href = xsd:anyURI > <!-- ##any --> </caption>
common attributes - defined in 8.12.1 Common Attributes
single node binding attributes - Selection of instance data node, defined in 8.12.2 Single Node Binding Attributes
xlink:href = xsd:anyURI - link to external caption
The caption specified can exist in instance data, in a remote
document, or as inline text. If multiple captions are specified in this
element, the order of preference is: ref, xlink:href,
inline.
An accessibility aid would typically speak the metadata encapsulated here when the containing form control gets focus.
8.12.4.2 help
The optional element help provides a convenient way to
attach help information to a form control. This is equivalent to a xforms:help event handler that responds with a <message
type="modeless">.
help><help (common attributes) (single node binding attributes) xlink:href = xsd:anyURI > <!-- ##any --> </help>
(common attributes) - defined in 8.12.1 Common Attributes
single node binding attributes - Selection of instance data node, defined in 8.12.2 Single Node Binding Attributes
xlink:href = xsd:anyURI - link to external help
The message specified can exist in instance data, in a remote
document, or as inline text. If multiple captions are specified in this
element, the order of precedence is: ref, xlink:href,
inline.
8.12.4.3 hint
The optional element hint provides a convenient way to
attach hint information to a form control. This is equivalent to a xforms:hint event handler that responds with a <message
type="ephemeral">.
hint><hint (common attributes) (single node binding attributes) xlink:href = xsd:anyURI > <!-- ##any --> </hint>
(common attributes) - defined in 8.12.1 Common Attributes
single node binding attributes - Selection of instance data node, defined in 8.12.2 Single Node Binding Attributes
xlink:href = xsd:anyURI - link to external hint
The message specified can exist in instance data, in a remote
document, or as inline text. If multiple captions are specified in this
element, the order of precedence is: ref, xlink:href,
inline.
8.12.4.4 alert
The optional element alert provides a convenient way to
attach alert or error information to a form control. This is equivalent to a xforms:alert event handler that responds with a <message
type="modal">.
alert><alert (common attributes) (single node binding attributes) xlink:href = xsd:anyURI > <!-- ##any --> </alert>
(common attributes) - defined in 8.12.1 Common Attributes
single node binding attributes - Selection of instance data node, defined in 8.12.2 Single Node Binding Attributes
xlink:href = xsd:anyURI - link to external alert
The message specified can exist at in instance data, in a remote
document, or as inline text. If multiple captions are specified in this
element, the order of precedence is: ref, xlink:href,
inline.
8.12.4.5 extension
Optional element extension is a container for
application-specific extension elements from any namespace other than the
XForms namespace. This specification does not define the processing of this
element.
extension><extension> <!-- ##other --> </extension>
For example, RDF metadata could be attached to an individual form control as follows:
<input ref="dataset/user/email" id="email-input">
<caption>Enter your email address</caption>
<extension>
<rdf:RDF xmlns:rdf="http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#">
<rdf:Description rdf:about="#email-input">
<my:addressBook>personal</my:addressBook>
</rdf:Description>
</rdf:RDF>
</extension>
</input>